The video game industry is reaching more people than ever — but this also means that ergonomic issues and injuries will happen more often to more people. How can gamers best prevent injury?
What do we mean by proper ergonomics?
At a very basic level, ergonomics, as defined by the International Ergonomics Association, is “the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions among humans and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data and methods to design in order to optimize human well-being and overall system performance.”
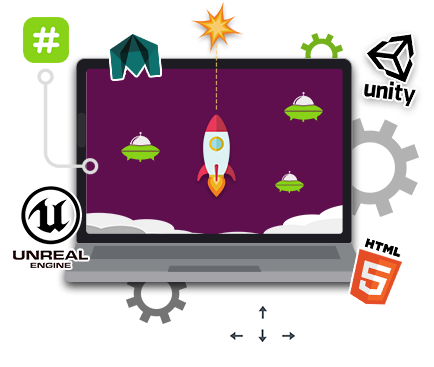
As it relates to gaming, ergonomics examines how players interact with their hardware and tools — and how the current standards may not be enough.
What ergonomic issues are gamers experiencing?
Repetitive strain wrist injuries remain among the most common issues for gamers, and have been since “Nintendinitis” was first coined in the mid-’80s. Due to repetitive actions such as continued button pressing, odd finger positioning, and rapid mouse movements/clicking, health issues in the hand and wrist are among the first to crop up for regular players.
Health experts have reported circulatory disorders, tenosynovitis, and even spinal damage as a result of continued joint stress. Less seriously, but perhaps more prevalent, is the simple loss of performance due to uncomfortable postures. And of course, a wrist brace can inhibit performance in even the slowest-paced video games. Poor ergonomics doesn’t just harm health, but victories in-game as well.
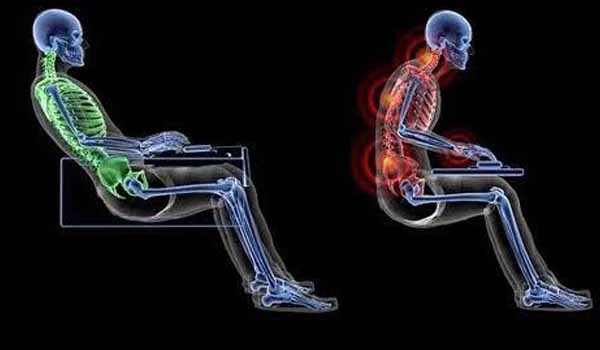
While repetitive strain issues are more common in action and shooter games, eye strain — staring at a screen too closely for too long — also affects players across genres. These issues have been recognized since at least the early 1990s, when a Japanese study suggested 60 minutes of playing time or less per day to avoid any injury.
An hour of daily gaming is hardly enough for many players, particularly in esports. These professional gamers average between 5-and-10 hours of practice per day, and their injuries are on the rise. Doctors are even suggesting esports players be treated like other college athletes when it comes to wrist, neck, and back pain.
The strain of esports can be so enormous that most players retire by the time they reach their mid-20s. But whether you’re gaming for an hour a week or three hours a day, it’s still important to consider ergonomics to prevent injuries.
Who’s responsible for gaming ergonomics?
Ergonomics is a two-way street between manufacturers who create and market the products and the consumers who use them.
Manufacturers
For manufacturers, all products operated by the human body should be physiologically appropriate and respect natural healthy posture. This is the only way to ensure health-sustainable operation of a console or PC during longer gaming sessions.
Products should be designed to support the natural posture of the body and the repetitive movements that are necessary to operate them. Manufacturers should ensure a back-friendly, wrist-friendly, and material-considered design. By working closely with physicians and scientists, gaming accessory companies can ensure their products will be used in the most appropriate way.
However, manufacturers can only do so much in product design. Ultimately, it’s up to the player to use their products in the correct way — and take note of other factors that help to prevent injuries.
Gamers
Arm position, seating posture, and playing style all come into effect when it comes to ergonomics. While manufacturers are responsible for providing ergonomic products, some physical damage comes only after a longer period of playing. You may not notice it at first, but you’ll want to make sure you take steps to avoid any future injuries.
Be sure to observe and follow the safety instructions provided with your equipment. You should also take breaks and follow preventive measures, e.g. stretching your arms and moving sufficiently to prevent latent strains.
The keyboard and mouse have been the PC gaming gold standard for decades, yet new options can increase comfort without sacrificing playability. If a flat keyboard doesn’t fit your gaming style, an ergonomic keyboard can help. These keyboards can adjust to the user and make typing more comfortable. The same goes for the mouse: an ergonomic mouse will fit the user’s hand better when scrolling and clicking — just like this one from Logitech. These features reduce strain, which can even lead to better performance while playing.
When playing in a seated position, the chair should support your back, and allow you to sit in a straight posture with your feet touching the floor. For shorter sessions, standing can be a good way to improve posture and overall health. An arm’s length away from the screen is generally fine.

If you’re worried about eye strain, Gunnar Optiks makes safety glasses designed to eliminate eye strain and block a computer’s blue light. In general, however, there should be enough light in the room to see the screen without squinting.
Of course, not everyone plays games at a desk. At nerdytec, we developed an ergonomic solution for comfortable PC or console gaming: our Couchmaster Cycon helps players keep an ergonomic posture from their couch or bed by not having to rest their keyboard on their lap.
These sorts of ergonomic tools can have a hugely beneficial impact on millions of gamers – provided they’re made widely available.

A healthier gaming lifestyle
The stereotype of gamers being unhealthy or lazier than the general population has been widely debunked. As with most stereotypes, these notions are borne out of broad assumptions and mischaracterized fears, all of which contribute to the lack of ergonomic equipment available for enthusiasts.
For decades, ergonomic accessories like mice and keyboards were only targeted toward office workers. Now that gamers finally have access to these same types of products, they can use these tools to stay fit while they pursue their passion alongside a healthy lifestyle — no carpal tunnel glove required.
credits: Roman Jakob (Cofounder and CTO at nerdytec)